
The NAT addresses allows to access and manage a virtual machine remotely without using a public IP address. Cloud-Bricks automatically sets up public forwarding ports specially for the SSH, RDP and HTTP protocols, so VMs can be accessed from Internet by using the Cloud Brick public IPv4 address as "gateway".
However, if a virtual machine requires to open a TCP or UDP service directly in the Internet and does not have a public IP address, you may use the port forwarding mechanism. This system can map a high port (>10.000) from the Cloud Brick node Public IPv4 address to an internal port in the virtual machine.
Example with MySql
For example, if we wish to make public the port 3306 in Internet (MySQL database) of a virtual machine that does not have a public IP address, but has an IPv4 NAT address.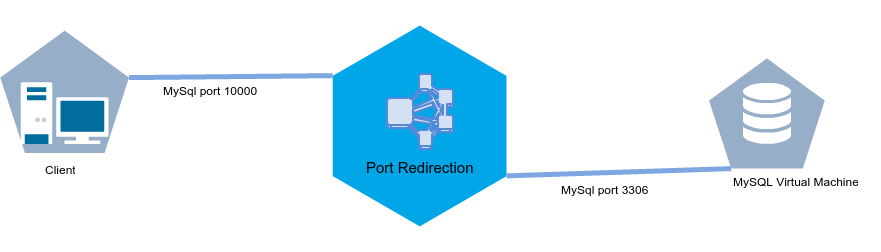 To do this, make sure that the MySQL service is running on port
3306, and give grant privileges to specific users from a remote host
with the command in SQL Console:
To do this, make sure that the MySQL service is running on port
3306, and give grant privileges to specific users from a remote host
with the command in SQL Console:
GRANT <privileges> ON *.* TO 'user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Configure Port Forwarding
Navigate to "Firewall>Port Forwarding" on the left menu.
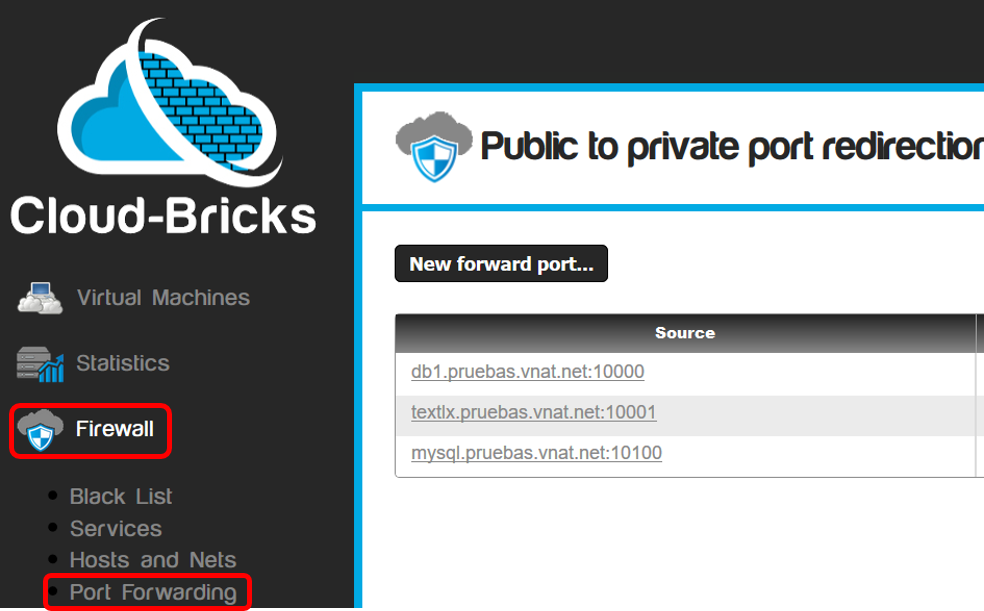
- Click the "New forward port..." button and choose the source port, the virtual machine, the destination port and the type of protocol (TCP or UDP).
- We will map Public Port 10000 to Private Port 3306 where mysql normally runs.
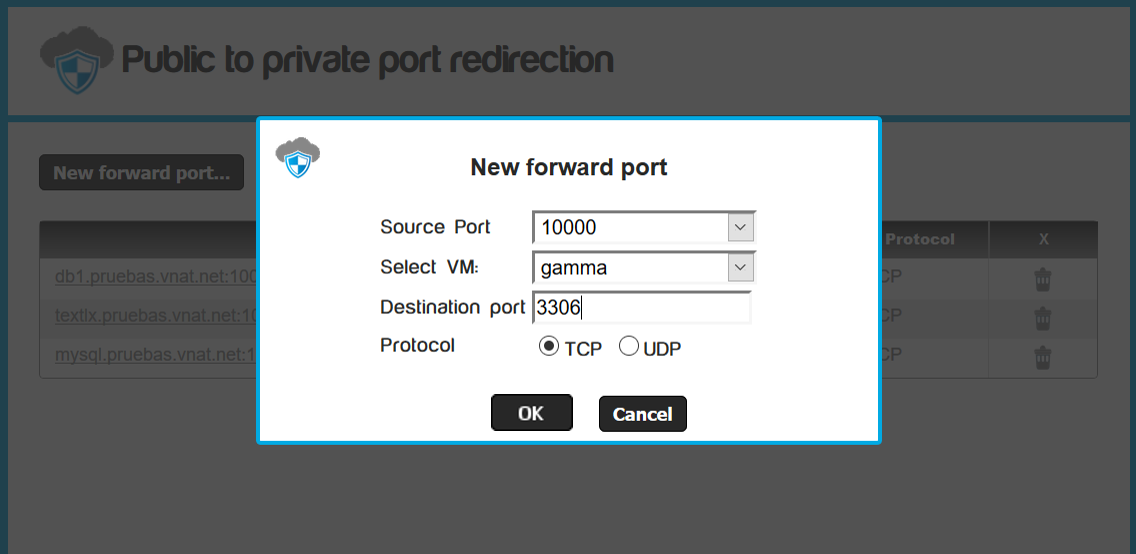
-
Then, click the "OK" button; after that click on the the "Commit changes" button.
Remote Access
To access a Port Forwarded service, you must use the hostname and port listed in the "Source" column of the port forwarding table.- Hostname format follows:
<virtual_machine_name>.<customer_name>.vnat.net - For this example hostname will be gamma.pruebas.vnat.net
- In this example, we use the public port 10000 mapped to the internal port 3306 in the virtual machine.
- Test the connection from an external machine with the command:
mysql -u root -p -h gamma.pruebas.vnat.net -P 10000

Important requirements
- For these connections to work, is mandatory for the virtual machine to have an IPv4 NAT address.
- Is VERY IMPORTANT to use always the specified hostname for client connections, and not the corresponding IP address directly, because that address may change.
- The port forwarding service is only available via IPv4, for IPv6 it is not necessary to use this mechanism because public IPv6 addresses are available for free.